Motivation is the fuel that drives human behavior, influencing everything from our daily routines to our long-term goals. But what exactly motivates us? Understanding the core motivators is key to unlocking potential in both personal and professional settings. The Motivators assessment, as highlighted in recent studies, delves into the seven universal dimensions that reveal why individuals behave the way they do.
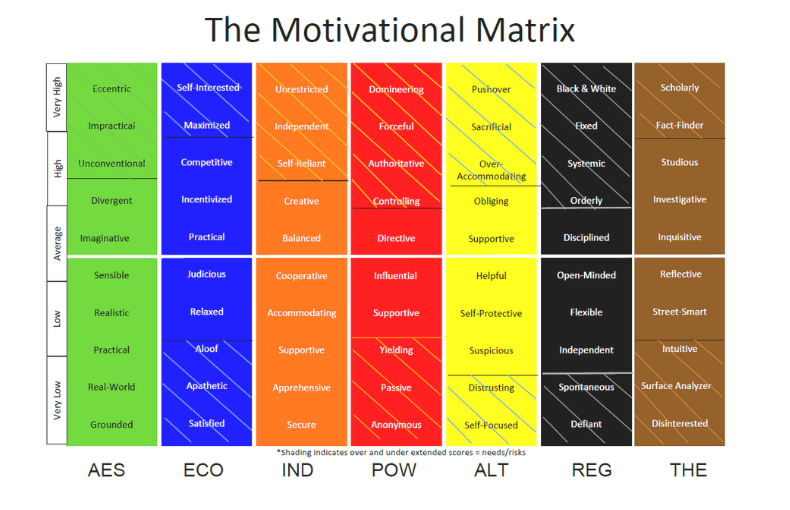
The Seven Universal Dimensions of Motivation
- Theoretical: This dimension is all about the pursuit of knowledge and understanding. Individuals driven by theoretical motivators are naturally curious and seek to learn and grow intellectually. They thrive in environments that challenge their minds and offer opportunities for continuous learning.
- Regulatory: Structure, order, and routine are the hallmarks of the regulatory dimension. People with high regulatory motivation prefer environments where clear rules and guidelines are in place. They value stability and predictability, which allows them to perform at their best.
- Individualistic: Independence and uniqueness are central to those motivated by individualistic needs. These individuals value their autonomy and are driven by the desire to stand out and express their individuality. They often excel in roles that allow for creativity and self-expression.
- Aesthetic: Those motivated by the aesthetic dimension are drawn to form, beauty, and balance. They seek harmony in their surroundings and value the quality of the experience over mere functionality. Aesthetic motivation often leads to a deep appreciation for art, nature, and the finer things in life.
- Economic: Practical results, financial gain, and return on investment are the primary concerns for those motivated by the economic dimension. These individuals are goal-oriented and often measure success in terms of tangible outcomes. They thrive in competitive environments where their efforts directly translate into rewards.
- Political: Control, power, and influence are the driving forces behind political motivation. Individuals with a high need for political influence seek positions of authority where they can guide and direct others. Leadership roles and decision-making responsibilities are where they feel most at home.
- Altruistic: Finally, the altruistic dimension is characterised by a desire to serve and help others. Altruistically motivated individuals are compassionate and often find fulfillment in roles that allow them to make a positive impact on the lives of others. They are the champions of empathy and are driven by a deep-seated need to contribute to the greater good.
Why Understanding Motivators Matters
Understanding these seven dimensions of motivation is crucial for several reasons. In the workplace, it allows employers to better match roles to individuals, optimising performance and satisfaction. It can also help in building more cohesive teams by aligning complementary motivators. On a personal level, knowing what drives you can lead to more fulfilling career choices and more satisfying personal relationships.
In summary, the Motivators assessment offers invaluable insights into the ‘why’ behind behavior. By understanding these universal dimensions, individuals and organisations alike can harness motivation to achieve greater success and fulfillment.